| Browse | Text search | Protein search | Domain search | Download | User manual | Related links | Citation & Contact |
The Haemolysin secretion/activation protein (ShlB/FhaC/HecB) Family [Function: Biogenesis/Secretion] Seed alignment | Full alignment | Pfam page | TC-DB page | ||||
The type V secretion pathway encompasses the autotransporter proteins (AT), the two-partner secretion system (TPS) and the type AT-2 family of proteins. TPS systems are composed of two separate proteins, with TpsA being the secreted protein and TpsB its specific transporter. The secreted proteins are exported in a Sec-dependent manner across the inner membrane, after which they cross the outer membrane with the help of their cognate transporters. Translocation appears to be folding-sensitive, indicating that TpsA proteins cross the periplasm and the outer membrane in non-native conformations and fold progressively at the cell surface. A major difference of the TPS pathways compared to the AT arises from the manner in which specificity is established between the secreted protein and its transporter. The TPS pathway has solved the question of specific recognition between the TpsA proteins and their transporters by the addition to the TpsA proteins of an N-proximal module, the conserved TPS domain, which represents a hallmark of the TPS pathway. The exoproteins of the TPS have been reported to be adhesins, haem-binding proteins, antigenic factors or haemolysins/cytolysins. The structure of the TPS domain has been solved and shows to fold as a ß helix. The crystal structure of the transmembrane domain of the Bordetella pertussis TpsB transporter (FhaC) has been resolved revealling a ß-barrel with 16 transmembrane strands. | ||||
Representative image: 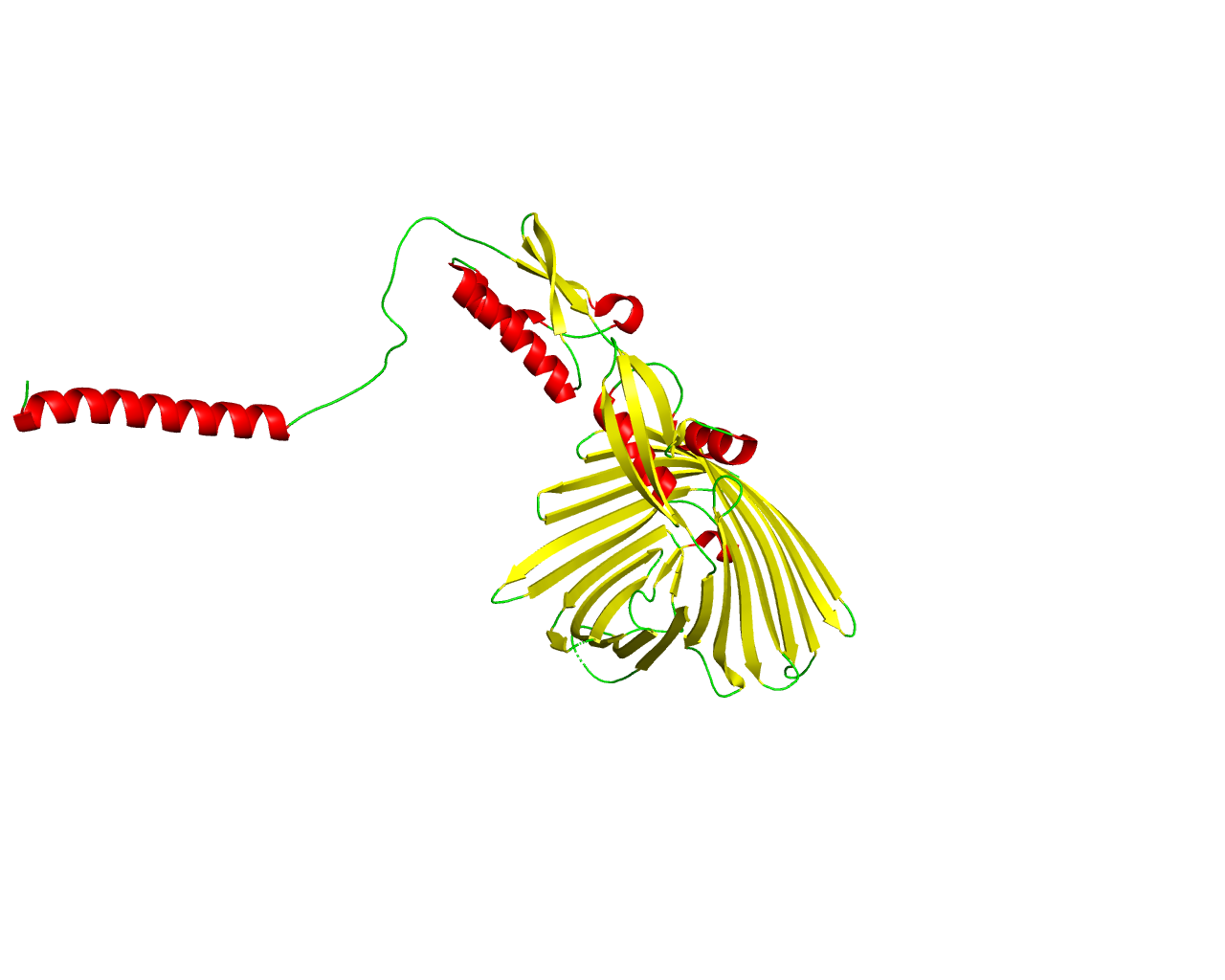 | ||||
| Literature references | ||||
Bordetella Filamentous Hemagglutinin, a Model for the Two-Partner Secretion Pathway Microbiol Spectr. 2019 Mar;7(2):10.1128/microbiolspec.PSIB-0024-2018. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.PSIB-0024-2018. PMID: 30927348 | ||||
Sequential unfolding of the hemolysin two-partner secretion domain from Proteus mirabilis Protein Sci. 2015 Nov;24(11):1841-55. doi: 10.1002/pro.2791. Epub 2015 Sep 9. PMID: 26350294 | ||||
Conserved Omp85 lid-lock structure and substrate recognition in FhaC Nat Commun. 2015 Jun 10;6:7452. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8452. PMID: 26058369 | ||||
Structure-function analysis reveals that the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Tps4 two-partner secretion system is involved in CupB5 translocation Protein Sci. 2015 May;24(5):670-87. doi: 10.1002/pro.2640. Epub 2015 Feb 24. PMID: 25641651 | ||||
An In Vitro Assay for Substrate Translocation by FhaC in Liposomes Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1329:111-25. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2871-2_8. PMID: 26427679 | ||||
Production and crystallization of bacterial type V secretion proteins Methods Mol Biol. 2013;966:205-22. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-245-2_13. PMID: 23299737 | ||||
Two-partner secretion of gram-negative bacteria: a single ß-barrel protein enables transport across the outer membrane J Biol Chem. 2012 Jan 20;287(4):2591-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.293068. Epub 2011 Dec 1. PMID: 22134917 | ||||
Functional importance of a conserved sequence motif in FhaC, a prototypic member of the TpsB/Omp85 superfamily FEBS J. 2010 Nov;277(22):4755-65. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07881.x. Epub 2010 Oct 19. PMID: 20955520 | ||||
Structure of the membrane protein FhaC: a member of the Omp85-TpsB transporter superfamily Science. 2007 Aug 17;317(5840):957-61. doi: 10.1126/science.1143860. PMID: 17702945 | ||||
Protein secretion through autotransporter and two-partner pathways Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Nov 11;1694(1-3):235-57. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2004.03.008. PMID: 15546669 | ||||
The autotransporter secretion system Res Microbiol. 2004 Mar;155(2):53-60. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2003.10.002. PMID: 14990256 | ||||
Autotransporter and two-partner secretion: delivery of large-size virulence factors by gram-negative bacterial pathogens Crit Rev Microbiol. 2004;30(4):275-86. doi: 10.1080/10408410490499872. PMID: 15646401 | ||||
| Proteins in this family with 3D-structure | ||||
View Entry | Description | Organism | Length | # strands |
